
Treating Skin Tears in Elderly Clients
Best Practices for Wound Care
When skin tears occur, especially in elderly individuals, it is crucial to choose wound care products that optimise healing and minimise further damage to fragile skin.
The ageing process affects the skin, leading to thinning of the epidermis, loss of collagen and elastin, and decreased activity of sweat and sebaceous glands, making older individuals more prone to skin tears (1)(2).
Skin tears result from various mechanical forces and require careful management to ensure optimal healing and prevent complications. Historically, basic island dressings and skin closure strips were commonly used, but evidence now suggests that this
approach may not be optimal (3)(4)(5).
Importance of Following Best Practice Guidelines
Prevention is key, but when a skin tear occurs, it is vital to follow current best practice guidelines for treatment (3).
The International Skin Tear Advisory Panel (ISTAP) best practice recommendations (2018) emphasise initial treatment goals, including controlling bleeding, cleansing and debriding the wound, managing infection and inflammation, considering moisture balance and exudate management, and monitoring wound edges for closure (5).
Choosing the Right Dressings for Skin Tears
Selecting the ideal dressing for managing skin tears requires
meeting several criteria, as outlined by ISTAP(5):
- Control bleeding
- Easy to apply and remove
- Avoid causing trauma on removal
- Provide a protective anti-shear barrier
- Optimize the physiological healing environment
- flexible and mould to contours
- Offer extended wear time
- Be non-toxic
- Be cost-effective
Silicone Foam Dressing
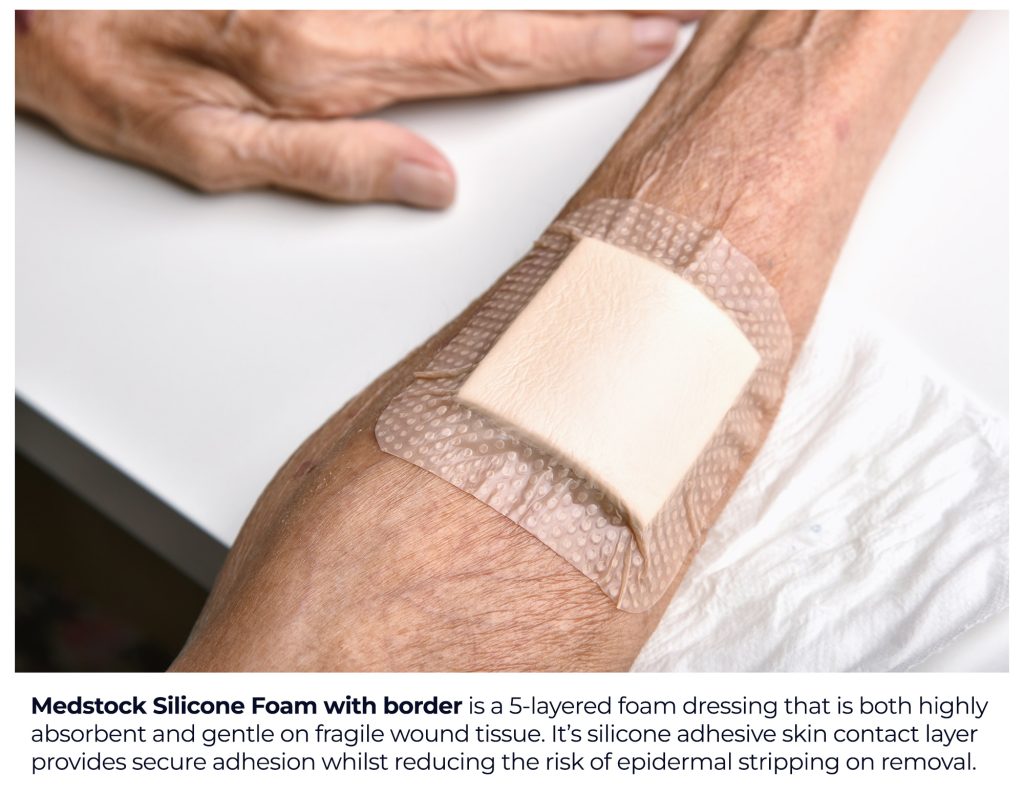
One highly recommended option after initial treatment is the use of silicone foam dressings, offering several benefits:
- Gentle Adhesion: Silicone foam dressings adhere gently to the skin without sticking to the wound bed, reducing pain and trauma during dressing changes(4).
- Reduces Risk of Maceration: Designed to manage exudate effectively, silicone foam dressings prevent maceration of surrounding skin, reducing the need for frequent dressing changes (3)(4).
- Comfort and Flexibility: Silicone foam dressings are flexible and conform to the body’s contours, providing comfort and accommodating movement(5).
- Maintains Moist Environment: These dressings help keep the wound moist, promoting healing and reducing scarring (4).
- Protection from Contaminants: Acting as a waterproof barrier, they reduce the risk of infection from external contaminants (4).
By considering these factors and following best practice guidelines, healthcare professionals can effectively treat and manage skin tears in elderly patients, promoting optimal wound healing and preventing future occurrences.

References:
- Holmes RF, Davidson MW, Thompson BJ, Kelechi TJ (2013) Skin tears: care and management of the older adult at home. Home Healthcare Nurse 31(2): 90-101
- LeBlanc K, Baranoski S, Christensen D et al (2016) The art of dressing selection: a consensus statement on skin tears and best practice. Adv Skin Wound Care 29(1): 32-46
- Moncrieff G, Van Onselen J, Young T (2015) The role of emollients in maintaining skin integrity. Wounds UK 11(1): 68-74
- Wounds UK (2012) Care of the older person’s skin: Best practice statement (2nd edition). (Accessed 7/6/24)
- ISTAP. (2018) The Prevention and Management of Skin Tears in Aged Skin. (Accessed 7/6/24)
Disclaimer
This website does not provide medical advice. The information, including but not limited to, text, graphics, images, and other material contained on this website, is for informational purposes only. No material on this site is intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health care provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment and before undertaking a new health care regimen. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.








